Copyright © 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006 Simon Mater, Thomas M. Eastep
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, with no Front-Cover, and with no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled “GNU Free Documentation License”.
2020/02/16
Table of Contents
Caution
This article applies to Shorewall 3.0 and later and to OpenVPN 2.0 and later. If you are running a version of Shorewall earlier than Shorewall 3.0.0 then please see the documentation for that release.
OpenVPN is a robust and highly configurable VPN (Virtual Private Network) daemon which can be used to securely link two or more private networks using an encrypted tunnel over the Internet. OpenVPN is an Open Source project and is licensed under the GPL. OpenVPN can be downloaded from http://openvpn.net/.
Unless there are interoperability issues (the remote systems do not support OpenVPN), OpenVPN is my choice any time that I need a VPN.
It is widely supported -- I run it on both Linux and Windows.
It requires no kernel patching.
It is very easy to configure.
It just works!
I recommend reading the VPN Basics article if you plan to implement any type of VPN.
Suppose that we have the following situation:
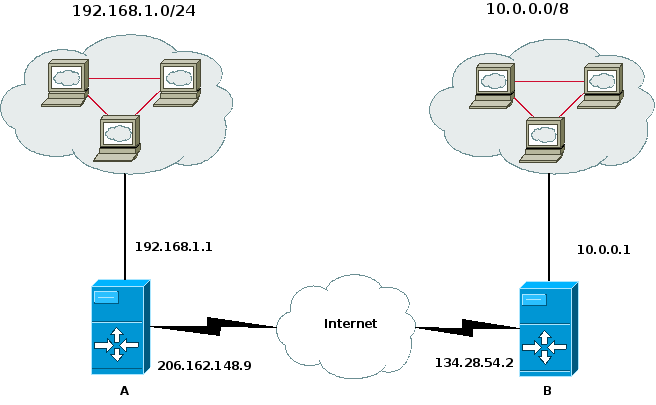
We want systems in the 192.168.1.0/24 subnetwork to be able to
communicate with the systems in the 10.0.0.0/8 network. This is
accomplished through use of the
/etc/shorewall/tunnels file and the
/etc/shorewall/policy file and OpenVPN.
While it was possible to use the Shorewall start and stop script to start and stop OpenVPN, I decided to use the init script of OpenVPN to start and stop it.
On each firewall, you will need to declare a zone to represent the
remote subnet. We'll assume that this zone is called “vpn”
and declare it in /etc/shorewall/zones on both
systems as follows.
/etc/shorewall/zones— Systems A & B#ZONE TYPE OPTIONS IN_OPTIONS OUT_OPTIONS vpn ipv4
On system A, the 10.0.0.0/8 will comprise the vpn zone.
In
/etc/shorewall/interfaceson system A:#ZONE INTERFACE OPTIONS vpn tun0
In /etc/shorewall/tunnels on system A, we need
the following:
#TYPE ZONE GATEWAY GATEWAY_ZONE openvpn net 134.28.54.2
This entry in /etc/shorewall/tunnels opens the
firewall so that OpenVPN traffic on the default port 1194/udp will be
accepted to/from the remote gateway. If you change the port used by
OpenVPN to 7777, you can define /etc/shorewall/tunnels like this:
/etc/shorewall/tunnels with port 7777:
#TYPE ZONE GATEWAY GATEWAY_ZONE openvpn:7777 net 134.28.54.2
Similarly, if you want to use TCP for your tunnel rather than UDP (the default), then you can define /etc/shorewall/tunnels like this:
/etc/shorewall/tunnels using TCP:
#TYPE ZONE GATEWAY GATEWAY_ZONE openvpn:tcp net 134.28.54.2
Finally, if you want to use TCP and port 7777:
/etc/shorewall/tunnels using TCP port 7777:
#TYPE ZONE GATEWAY GATEWAY_ZONE openvpn:tcp:7777 net 134.28.54.2
This is the OpenVPN config on system A:
dev tun local 206.162.148.9 remote 134.28.54.2 ifconfig 192.168.99.1 192.168.99.2 route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 192.168.99.2 tls-server dh dh1024.pem ca ca.crt cert my-a.crt key my-a.key comp-lzo verb 5
Similarly, On system B the 192.168.1.0/24 subnet will comprise the vpn zone
In
/etc/shorewall/interfaceson system B:#ZONE INTERFACE BROADCAST OPTIONS vpn tun0
In /etc/shorewall/tunnels on system B, we
have:
#TYPE ZONE GATEWAY GATEWAY_ZONE openvpn net 206.191.148.9
And in the OpenVPN config on system B:
dev tun local 134.28.54.2 remote 206.162.148.9 ifconfig 192.168.99.2 192.168.99.1 route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 tls-client ca ca.crt cert my-b.crt key my-b.key comp-lzo verb 5
You will need to allow traffic between the “vpn” zone and the “loc” zone on both systems -- if you simply want to admit all traffic in both directions, you can use the policy file:
/etc/shorewall/policyon systems A & B#SOURCE DEST POLICY LOG LEVEL loc vpn ACCEPT vpn loc ACCEPT
On both systems, restart Shorewall and start OpenVPN. The systems in the two masqueraded subnetworks can now talk to each other.
OpenVPN 2.0 provides excellent support for roadwarriors. Consider the setup in the following diagram:
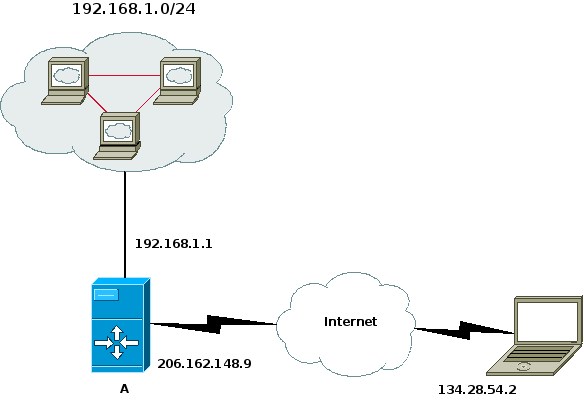
On the gateway system (System A), we need a zone to represent the remote clients — we'll call that zone “road”.
/etc/shorewall/zones— System A:#ZONE TYPE OPTIONS IN_OPTIONS OUT_OPTIONS road ipv4
On system A, the remote clients will comprise the road zone.
In
/etc/shorewall/interfaceson system A:#ZONE INTERFACE OPTIONS road tun+
In /etc/shorewall/tunnels on system A, we need
the following:
#TYPE ZONE GATEWAY GATEWAY_ZONE openvpn:1194 net 0.0.0.0/0
If you are running Shorewall 2.4.3 or later, you might prefer the
following in /etc/shorewall/tunnels on system A.
Specifying the tunnel type as openvpnserver has the advantage that the VPN
connection will still work if the client is behind a gateway/firewall that
uses NAT.
#TYPE ZONE GATEWAY GATEWAY_ZONE openvpnserver:1194 net 0.0.0.0/0
We want the remote systems to have access to the local LAN — we do
that with an entry in /etc/shorewall/policy (assume
that the local LAN comprises the zone “loc”).
#SOURCE DESTINATION POLICY road loc ACCEPT
The OpenVPN configuration file on system A is something like the following:
dev tun server 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 dh dh1024.pem ca /etc/certs/cacert.pem crl-verify /etc/certs/crl.pem cert /etc/certs/SystemA.pem key /etc/certs/SystemA_key.pem port 1194 comp-lzo user nobody group nogroup ping 15 ping-restart 45 ping-timer-rem persist-tun persist-key push "route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0" verb 3
Configuration on the remote clients follows a similar line. We define a zone to represent the remote LAN:
/etc/shorewall/zones— System B:#ZONE TYPE OPTIONS IN OUT # OPTIONS OPTIONS home ipv4
On system A, the hosts accessible through the tunnel will comprise the home zone.
In
/etc/shorewall/interfaceson system B:#ZONE INTERFACE BROADCAST OPTIONS home tun0
In /etc/shorewall/tunnels on system B, we need
the following:
#TYPE ZONE GATEWAY GATEWAY_ZONE openvpn:1194 net 206.162.148.9
Again, if you are running Shorewall 2.4.3 or later, in
/etc/shorewall/tunnels on system B you might
prefer:
#TYPE ZONE GATEWAY GATEWAY_ZONE openvpnclient:1194 net 206.162.148.9
We want the remote client to have access to the local LAN — we do
that with an entry in /etc/shorewall/policy.
#SOURCE DESTINATION POLICY $FW home ACCEPT
The OpenVPN configuration on the remote clients is along the following line:
dev tun remote 206.162.148.9 up /etc/openvpn/home.up tls-client pull ca /etc/certs/cacert.pem cert /etc/certs/SystemB.pem key /etc/certs/SystemB_key.pem port 1194 user nobody group nogroup comp-lzo ping 15 ping-restart 45 ping-timer-rem persist-tun persist-key verb 3
If you want multiple remote clients to be able to communicate openly with each other then you must:
Include the client-to-client directive in the server's OpenVPN configuration; or
Specify the routeback option on the
tun+device in /etc/shorewall/interfaces.
The information in this section was contributed by Nicola Moretti.
If your local lan uses a popular RFC 1918 network like 192.168.1.0/24, there will be times when your roadwarriors need to access your lan from a remote location that uses that same network.
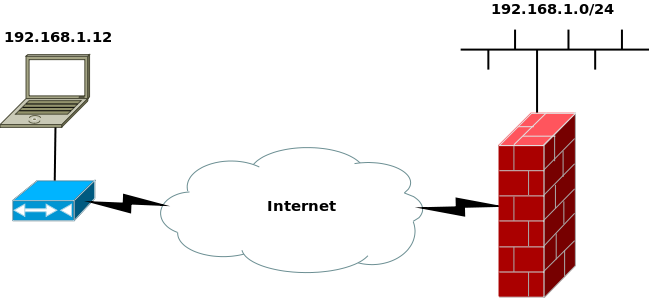
This may be accomplished by configuring a second server on your firewall that uses a different port and by using NETMAP in your Shorewall configuration. The server configuration in the above diagram is modified as shown here:
dev tun server 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 dh dh1024.pem ca /etc/certs/cacert.pem crl-verify /etc/certs/crl.pem cert /etc/certs/SystemA.pem key /etc/certs/SystemA_key.pem port 1195 comp-lzo user nobody group nogroup ping 15 ping-restart 45 ping-timer-rem persist-tun persist-key push "route 172.20.1.0 255.255.255.0" verb 3
In /etc/shorewall/netmap, put these
entries:
#TYPE NET1 INTERFACE NET2 SNAT 192.168.1.0/24 tun1 172.20.1.0/24 DNAT 172.20.1.0/24 tun1 192.168.1.0/24
The roadwarrior can now connect to port 1195 and access the lan on the right as 172.20.1.0/24.
While OpenVPN supports tunneling of IPv6 packets, the version of the code that I run under OS X on my Macbook Pro does not support that option. Nevertheless, I am able to take IPv6 on the road with me by creating a 6to4 tunnel through the OpenVPN IPv6 tunnel. In this configuration, the IPv4 address pair (172.20.0.10,172.20.0.11) is used for the OpenVPN tunnel and (2001:470:e857:2::1,2001:470:e857:2::2) is used for the 6to4 tunnel.
Here are my config files:
Server (conventional routed server config):
dev tun local 70.90.191.121 server 172.20.0.0 255.255.255.128 dh dh1024.pem ca /etc/certs/cacert.pem crl-verify /etc/certs/crl.pem cert /etc/certs/gateway.pem key /etc/certs/gateway_key.pem port 1194 comp-lzo user nobody group nogroup keepalive 15 45 ping-timer-rem persist-tun persist-key client-config-dir /etc/openvpn/clients ccd-exclusive client-to-client push "route 172.20.1.0 255.255.255.0" verb 3In the CCD file for the Macbook Pro:
ifconfig-push 172.20.0.11 172.20.0.10From
/etc/network/interfaces(very standard 6to4 tunnel configuration):auto mac iface mac inet6 v4tunnel address 2001:470:e857:2::1 netmask 64 endpoint 172.20.0.11 local 172.20.1.254Note that while the remote endpoint (172.20.0.11) is also the remote endpoint of the OpenVPN tunnel, the local endpoint (172.20.1.254) of the 6to4 tunnel is not the local endpoint of the OpenVPN tunnel (that;s 172.20.0.10). 172.20.1.254 is the IPv4 address of the Shorewall firewall's LAN interface.
The following excerpts from the Shorewall configuration show the parts of that configuration that are relevant to these two tunnels (bold font). This is not a complete configuration.
/etc/shorewall/zones:#ZONE TYPE fw firewall loc ip #Local Zone drct:loc ipv4 #Direct internet access net ipv4 #Internet vpn ipv4 #OpenVPN clients
/etc/shorewall/interfaces:#ZONE INTERFACE BROADCAST OPTIONS loc INT_IF detect dhcp,logmartians=1,routefilter=1,physical=$INT_IF,required,wait=5 net COM_IF detect dhcp,blacklist,optional,routefilter=0,logmartians,proxyarp=0,physical=$COM_IF,nosmurfs vpn TUN_IF+ detect physical=tun+,routeback - sit1 - ignore - mac - ignore - EXT_IF - ignore - lo - ignore
/etc/shorewall/tunnels:#TYPE ZONE GATEWAY GATEWAY # ZONE openvpnserver:udp net 6to4 net 6to4 vpnSimilarly, here are excerpts from the Shorewall6 configuration.
/etc/shorewall6/zones:#ZONE TYPE OPTIONS IN OUT # OPTIONS OPTIONS fw firewall net ipv6 loc ipv6 rest ipv6
/etc/shorewall6/interfaces:#ZONE INTERFACE BROADCAST OPTIONS net sit1 detect tcpflags,forward=1,nosmurfs,routeback loc eth4 detect tcpflags,forward=1 loc mac detect tcpflags,forward=1 rest eth+Note that in the IPv6 firewall configuration, the remove Macbook Pro is considered to be part of the local zone (loc).
Client (conventional routed client config):
client dev tun proto udp remote gateway.shorewall.net 1194 resolv-retry infinite nobind persist-key persist-tun mute-replay-warnings ca ca.crt cert mac.crt key mac.key ns-cert-type server comp-lzo verb 3 up /Users/teastep/bin/up down /Users/teastep/bin/down
/Users/teastep/bin/up:#!/bin/bash LOCAL_IP=172.20.0.11 LOCAL_IPV6=2001:470:e857:2::2 REMOTE_IP=172.20.1.254 REMOTE_IPV6=2001:470:e857:2::1 TUNNEL_IF=gif0 if [ $(ifconfig gif0 | wc -l ) -eq 1 ]; then # # Tunnel interface is not configured yet # /sbin/ifconfig $TUNNEL_IF tunnel $LOCAL_IP $REMOTE_IP /sbin/ifconfig $TUNNEL_IF inet6 $LOCAL_IPV6 $REMOTE_IPV6 prefixlen 128 else /sbin/ifconfig $TUNNEL_IF up fi /sbin/route -n add -inet6 default $REMOTE_IPV6 > /dev/null 2>&1
/Users/teastep/bin/down:#!/bin/bash TUNNEL_IF=gif0 /sbin/ifconfig $TUNNEL_IF down /sbin/route -n delete -inet6 default > /dev/null 2>&1
If you want to use a bridged OpenVPN configuration rather than a routed configuration, then follow any of the available HOWTOs to set up the bridged configuration. Then:
In your current Shorewall two-interface configuration, replace references to your internal interface with the name of the bridge; and
Set the routeback option in the bridge's entry in /etc/shorewall/interfaces; end
Add this entry to /etc/shorewall/tunnels:
#TYPE ZONE GATEWAY GATEWAY_ZONE openvpnserver:1194 net 0.0.0.0/0
This will make the roadwarrior part of your local zone.
Occasionally, the need arises to have a single LAN span two different geographical locations. OpenVPN allows that to be done easily.
Consider the following case:
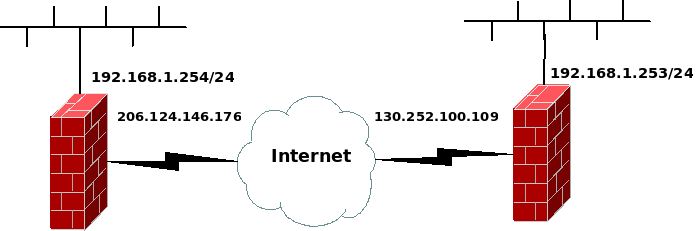
Part of the 192.168.1.0/24 network is in one location and part in another. The two LANs can be bridged with OpenVPN as described in this section. This example uses a fixed shared key for encryption.
OpenVPN configuration on left-hand firewall:
remote 130.252.100.109 dev tap0 secret /etc/openvpn/bridgekey
OpenVPN configuration on right-hand firewall:
remote 206.124.146.176 dev tap0 secret /etc/openvpn/bridgekey
The bridges can be created by manually making the tap device tap0 and bridgeing it with the local ethernet interface. Assuming that the local interface on both sides is eth1, the following stanzas in /etc/network/interfaces (Debian and derivatives) will create the bridged interfaces.
Note
The stanzas below were written before bridges could be defined in /etc/network/interfaces. For current usage, see bridge-utils-interfaces (5).
/etc/network/interfaces on the left-hand firewall:
iface br0 inet static
pre-up /usr/sbin/openvpn --mktun --dev tap0
pre-up /usr/sbin/brctl addbr br0
address 192.168.1.254
network 192.168.1.0
broadcast 192.168.1.255
netmask 255.255.255.0
post-up /sbin/ip link set tap0 up
post-up /usr/sbin/brctl addif br0 tap0
post-up /sbin/ip link set eth1 up
post-up /usr/sbin/brctl addif br0 eth1
post-down /usr/sbin/brctl delbr br0
post-down /usr/sbin/openvpn --rmtun --dev tap0
post-down /sbin/ip link set eth1 down /etc/network/interfaces on the right-hand firewall:
iface br0 inet static
pre-up /usr/sbin/openvpn --mktun --dev tap0
pre-up /usr/sbin/brctl addbr br0
address 192.168.1.253
network 192.168.1.0
broadcast 192.168.1.255
netmask 255.255.255.0
post-up /sbin/ip link set tap0 up
post-up /usr/sbin/brctl addif br0 tap0
post-up /sbin/ip link set eth1 up
post-up /usr/sbin/brctl addif br0 eth1
post-down /usr/sbin/brctl delbr br0
post-down /usr/sbin/openvpn --rmtun --dev tap0
post-down /sbin/ip link set eth1 down The Shorewall configuration is just a Simple Bridge.